Personalization and Registration¶
In order for a device such as a register, tablet, handheld, etc. to be used within the context of the Jumpmind Commerce solution, that device must first be personalized and registered to the system. These personalization and registration processes define the functional context of the device to the system including where the device is located, a name for the device, a unique identifer to identify this specific device, the functional application you want the device to run, and last but not least, information about where that system needs to connect to register and access the overall application.
Concepts¶
-
Personalization - The process of identifying and tailoring a device to a specific location and functional application within the sytem. This amounts to providing personalization parameters that identify the device, its name, the application, desired to be run, application sever and port, etc.
-
Personalization Parameters - The application parameters that tell the system how to tailor a device for specific use within the system
-
Manual Personalization - A mechanism by which a user can provide personalization parameters for a device at initial startup through the user interface by manually entering these parameters via a series of screens.
-
Auto Personalization - A mechanism by which the system automatically determines personalization parameters for a device based on data previously entered or being provided for the device. In this scenario, no user interface is used to manually provide personalization parameters
-
Personalization Provider - Different mechanisms or implementations provided out of the box to provide personalization parameters for a device, either manual or automatic (Auto)
-
Registration - The process of taking personalization parameters, and registering and authenticating a specific device to the system. This registration information is stored both on the application server where the device connects, as well as on the device, such that subsequent uses of the device can identify the device and authenticate it to the system.
-
Registration Information - Information provided by the registration process that is stored on the device for future use including functional context of the device and authentication information.
Overview¶
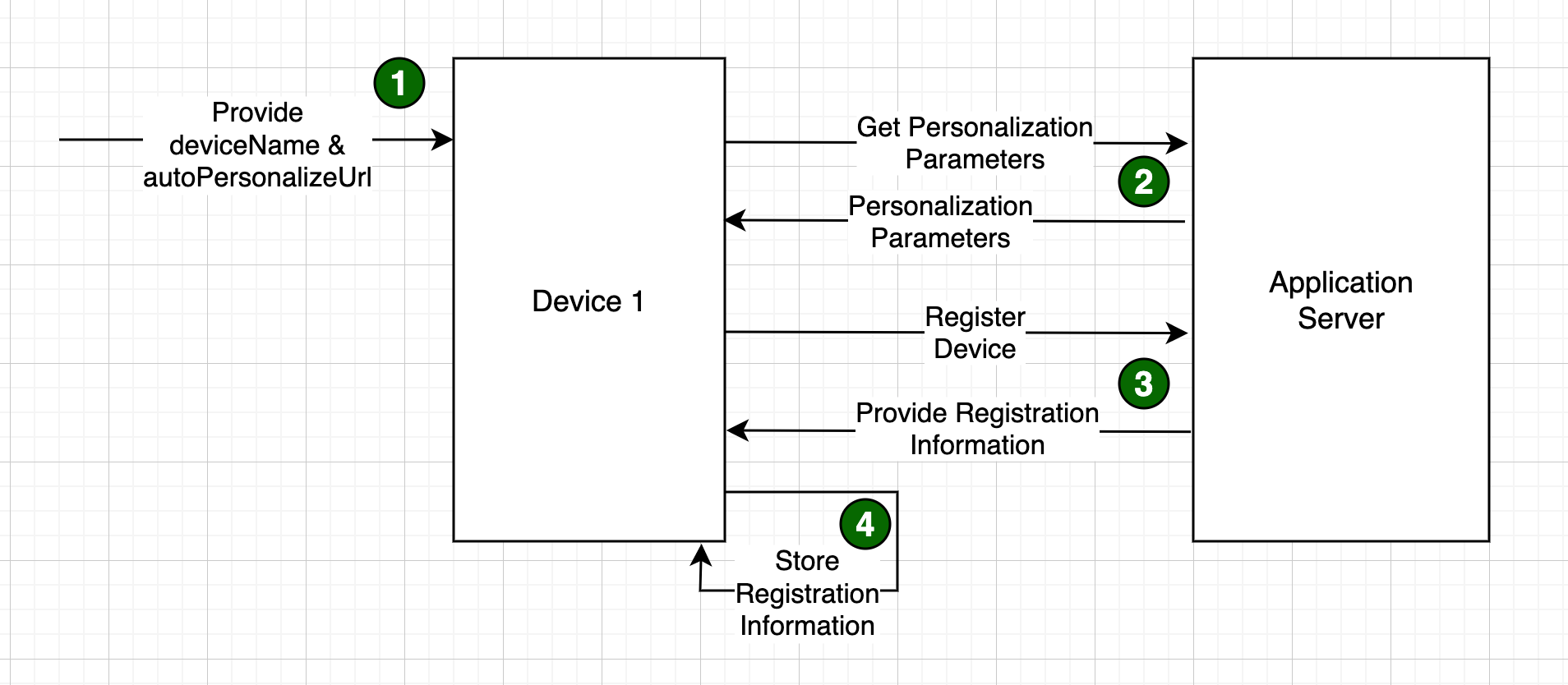
The process of personalization and registration is either a three or four step process depending on how the system is conigured and how the personalization parameters are obtained / provided. In its simplest three step form, the personalization and registration process looks as follows:
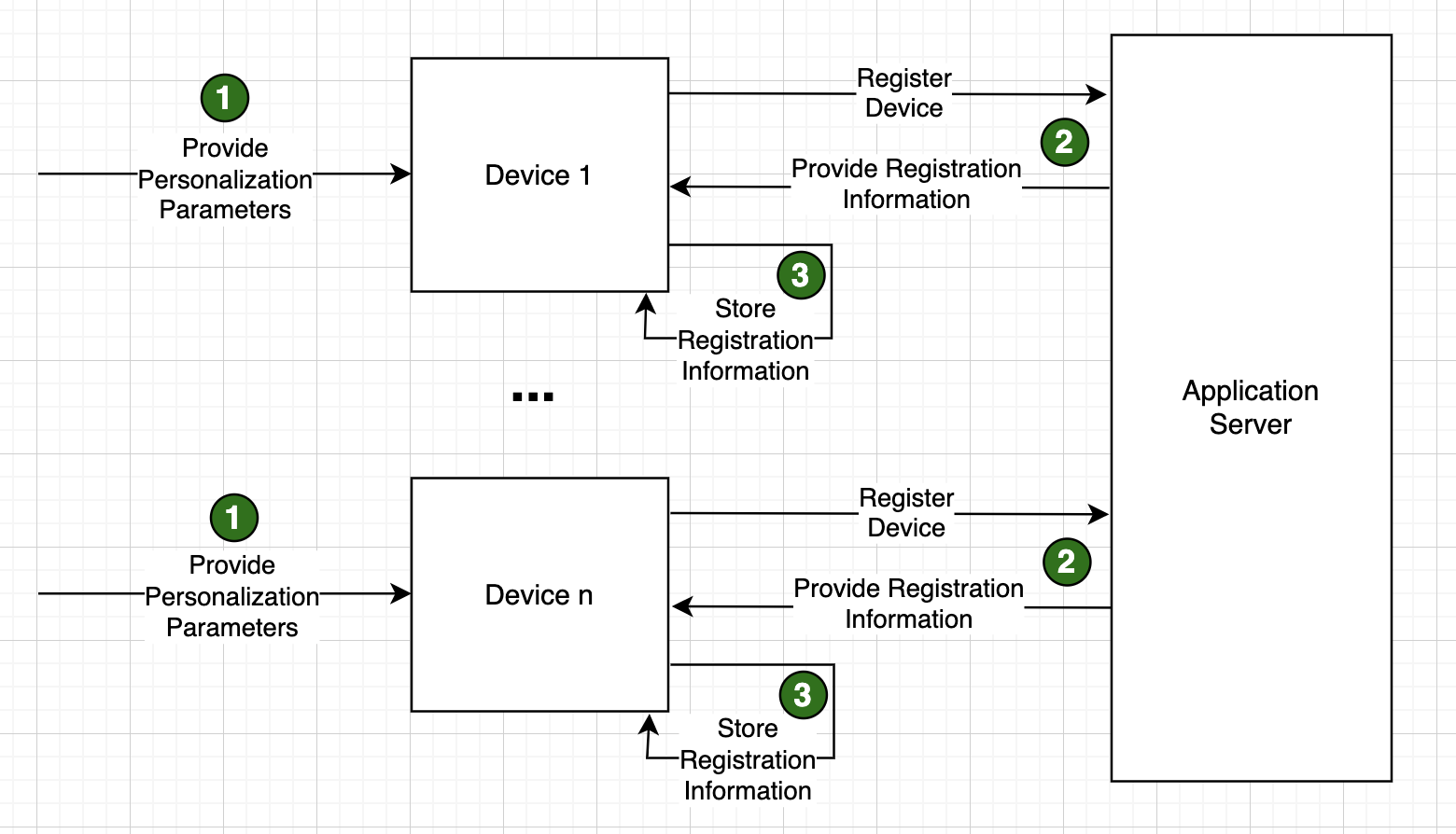
In this simplest form, all personalization parameters are provided (step 1) and those parameters are used to call a service on the application server which registers the device and passes back certain registration information including an authorization token back to the device (Step 2). The final step in the process is for the application on the device to store that registration information for later use. For example, every time a device attempts to connect to the system, it must provide its device_id and authorization token to authenticate to the application.
Personalization Parameters¶
The full list of personalization parameters to be provided in the simple three step process are as follows. Parameters indicated by the red asterisk are required parameters.
-
Device Name (deviceName)* - The name of the device that is to be personalized and registered with the system. Most times this name matches the physical name of the device for tracking and traceability purposes, but note that is not a requirement.
-
Server URL (serverUrl)* - The protocol, server name, and port of the server to which this device will both register (step 2 of the personalization process) and connect to for its application web server. Usually a DNS name pointing to the server.
-
Device Id (deviceId)* - The identifier for the device that is used to log and track all information about and transactions from this device. A common nomenclature pattern used for this is 5 digit business unit concatenated with a "-" and the three digit device number. I.E. for a device running in business unit (store) 777 as register 1, the device id in this example would be 00777-001.
-
Application Id (appId)* - The application desired to run on this device (pos,customerdisplay,selfcheckout,mobilemgmt,pricechecker)
-
Parent Device Id (parentDeviceId) - If a device is personalized and registered to run with an Application Id of customerdisplay, the parent device id is the deviceId of the device that is running pos, for which this device is providing customer display capabilities.
-
Parent App Id (parentAppId) - The applicationId that the pardentDeviceId is running.
-
Business Unit Id (businessUnitId)* - The business unit context in which this device will run. Typically a store, represented by a five digit store number (i.e. 00777)
-
Failover Server Url 1 (failoverServerUrl1) - If more than one web application server is available for the device, the failover server address (including protocol, server name, and port) is used to provide failover server that can be reached if the primary server (serverAddress) is not available.
-
Failover Server Url 2 (failoverServerUrl2) - If more than one web application server is available for the device, the failover server address (including protocol, server name, and port) is used to provide failover server that can be reached if the primary server (serverAddress) is not available.
-
Failover Server Url 3 (failoverServerUrl3) - If more than one web application server is available for the device, the failover server address (including protocol, server name, and port) is used to provide failover server that can be reached if the primary server (serverAddress) is not available.
Personalization Providers¶
As discussed in the Concepts section above, JMC provides multiple personalization providers out of the box for providing and obtaining personalization parameters for a given device. Each one of those providers is described in detail below.
Manual Personalization Provider¶
The manual personalization provider allows a user to specify personalization parameters via the application user interface when the application on the device starts for the first time, and any subsequent time if stored registration information on the device is cleared, either through the developer tools or by uninstalling and re-installing the application. This is the only personalization provider that is considered "manual" because there are manual steps to be taken when the application initializes for the first time on the device. All other providers are considered "automatic" as the personalization parameters are provided systemically through some other means.
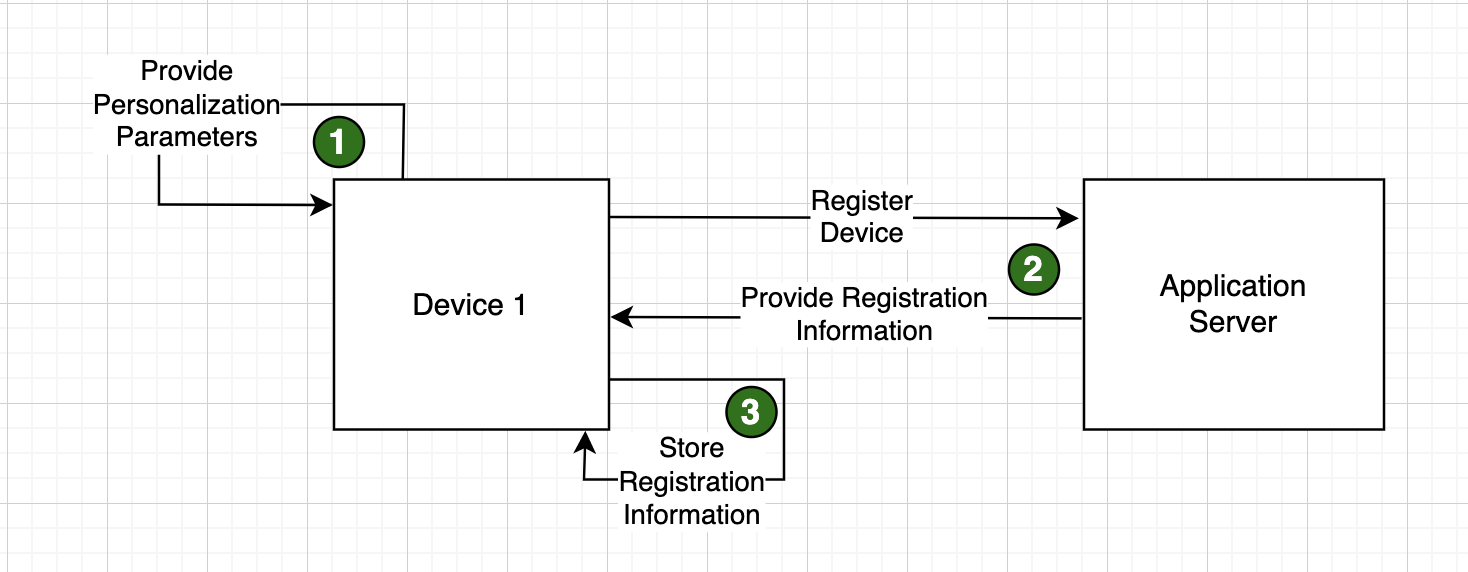
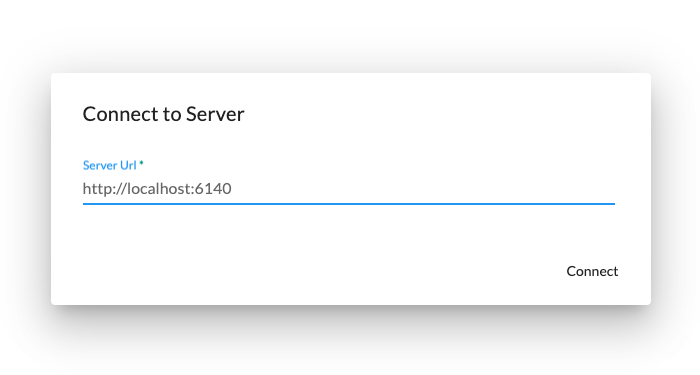
When using the manual personalization provider, the following three steps are used to personalize the device. Screen 1
allows the user to specify the server URL where the application server is running and listening on. If you are using
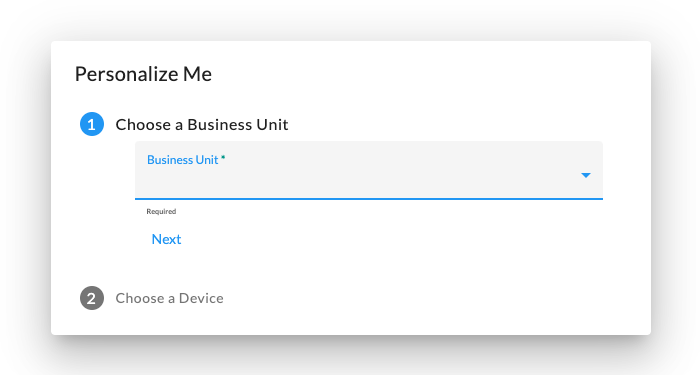
SSL, make sure to specify https for the protocol. Screen 2 allows
the user to specify the business unit the device will be operating within, and screen 3 allows the user to specify the device
identifier for the device.
| Screen 1 | Screen 2 | Screen 3 |
|---|---|---|
 |
 |
 |
Once the personalization parameters above are specified, the device registers with the server using those parameters and stores its registration information locally when complete.
It is important to note that not all personalization parameters can be specified with the manual personalization process including tag information, failover servers and ports, device names, etc. The parameters that can be supplied are:
| Screen Element | Personaliation Parameter |
|---|---|
| Server Url | serverUrl |
| Business Unit | businessUnitId |
| Device | deviceId |
| App Id | appId |
QueryParams Auto Personalization Provider¶
The QueryParams personalization provider can be used in one of two ways. The first is to pass all required personalization parameters to the application on the command line when invoking the client application on the device. This is very similar to the manual personalization provider, but instead of providing personalization parameters through the user interface, they are passed on the command line. An example of passing personalization on the command line in a Microsoft Windows environment looks as follows:
commerce-client.exe "--queryParams=deviceId=%installationId%&serverUrl=http://localhost:6140&appId=pos&brandId=default&deviceType=default"
The second way the QueryParams personalization provider can be used is by passing only two parameters on the command line:
-
deviceName - The name of the device attempting to personalize and register
-
autoPersonalizeUrl - The url of a web service that will provide personalization parameters for this device. This can be a custom service or one of the out of the box Jumpmind services/endpoints for providing personalization parameters. This is considered a 4 step personalization and registration process as depicted below.
commerce-client.exe "--queryParams=deviceName=device123&autoPersonalizeUrl=http://myServer.myDomain.com:6140/rest/admin/personalizeMe"
For step #2, the new step in the process that gets full personalization parameters for a device based on the device name, the JMC product provides a standard interface and two different implementations / endpoints to provide this functionality. The interface looks as follows:
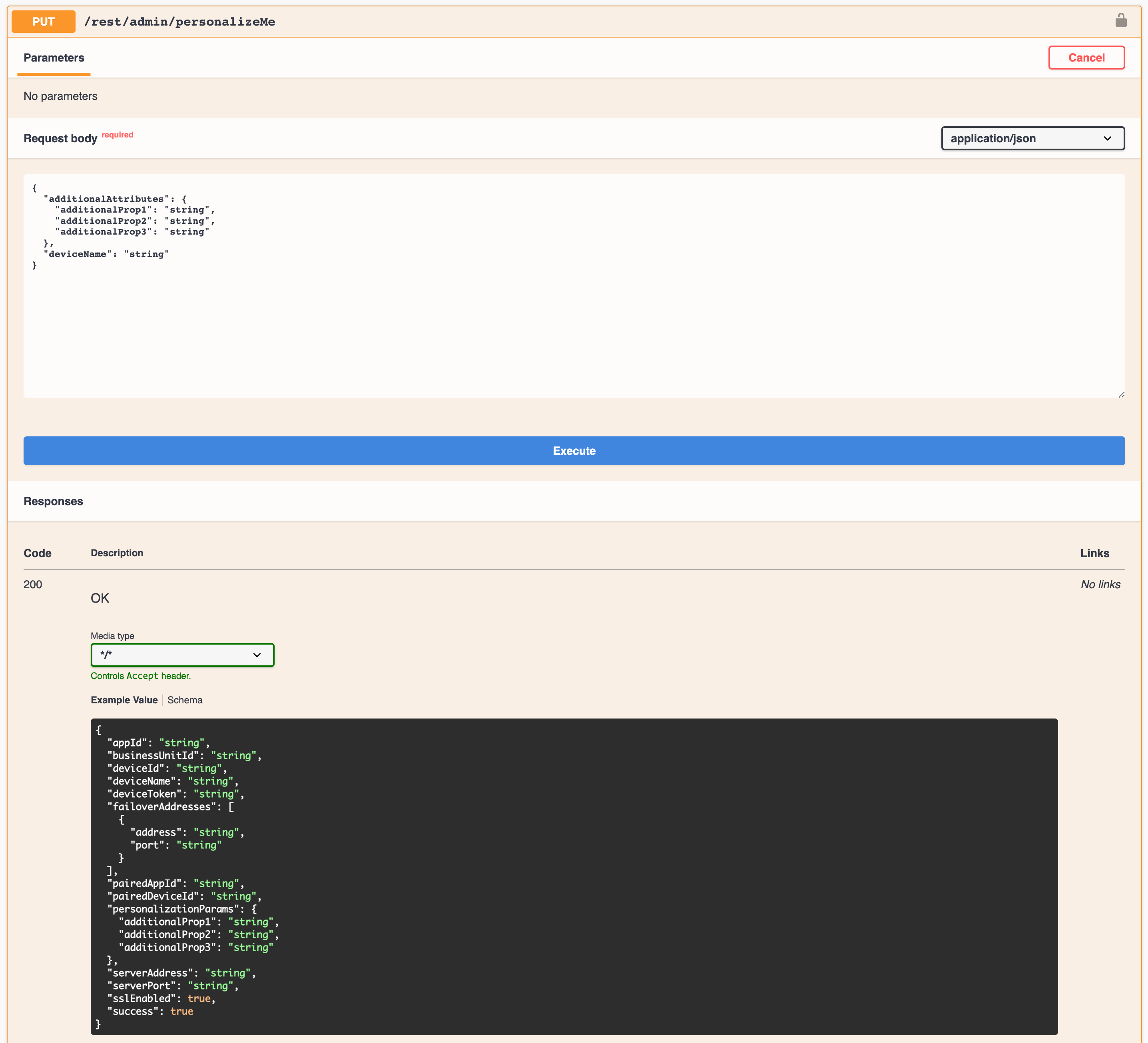
The two different endpoint implementations provided out of the box for this interface are:
- GetDevicePersonalizationModelEndpoint - In this implementation, the service obtains personalization parameters
for a device from the
dev_device_personalizationtable based on a lookup of the passed in deviceName (device_name). In the following example, a deviceName of "US005243MR130", looks up personalization parameters in thedev_device_personalizationtable and returns the personalization parameters as shown below. By leveraging this endpoint, customers can predefine the personalization parameters for every device by device name in thedev_device_personalizationtable such that when a device gets to the field, it can look up its personalization parameters by name. This is the default implementation for this endpoint, so no additional configuration is needed to setup and use this endpoint.

- ParseDevicePersonalizationEndpoint - The parse device personalization endpoint is a simple endpoint that allows the
customer to configure a groovy expression to derive required personalization parameters from the deviceName. The groovy
expression configuration is specified in yml configuration at
openpos.autoPersonalization.config.parseDevicePersonalizationConfig. Groovy expressions can be provided for deviceId, appId, hostName and map of other personalizationParams. As an example, with a deviceName of "05243-001|pos", a configuration parameter of deviceId: "deviceName.substring(0, 9)" and appId: "deviceName.substring(10)" would result in the endpoint returning a deviceId of "05243-001" and an appId of "pos". To configure this endpoint, the /admin/personalizeMe should be configured to implementation: "parsed"
EnterpriseConfig Auto Personalization Provider¶
The EntepriseConfig personalization provider allows an alternate method of specifying the deviceName and autoPersonalizeUrl for iOS and Android devices such that personalization parameters can be obtained from the GetDevicePersonalizationModelEndpoint, the ParseDevicePersonalizationModelEndpoint or another customer specific endpoint. It's important to note that unlike the QueryParams personalization provider where all personalization parameters can be specified, in the Enterprise Config personalization provider, only the deviceName and autoPersonalizeUrl can be specified (i.e. it requires a 4 step personalization and registration process) where all personalization parameters come from an endpoint implementation of the /rest/admin/personalizeMe interface.
The EnterpriseConfig personalization provider allows passing deviceName and autoPersonalizeUrl through the customer's Mobile Device Management (MDM) solution via Managed App Configuration. Managed App Configuration is mechanism by which deployment parameters for an application can be specified in the MDM solution, installed and configured when the application is deployed and then accessed by the application for use within the application itself. When specifying these parameters in the customer's MDM, specify the following two parameters:
-
deviceName - The name of the device attempting to personalize and register.
-
autoPersonalizeUrl - The url of a web service that will provide personalization parameters for this device. See information in the QueryParams section of this document for additional details.
Most MDM providers provide a user interface or will allow the import of an XML file for definition of the configuration parameters to be provided to the application. The following is a sample XML configuration that can be uploaded to the MDM provider for parameter definition and default values.
<managedAppConfiguration>
<version>1</version>
<bundleId>com.jumpmind.commerce.dev</bundleId>
<dict>
<string keyName="deviceName">
<defaultValue>
<value>{SerialNumber}</value>
</defaultValue>
</string>
<string keyName="autoPersonalizeUrl">
<defaultValue>
<value>https://myServer.myDomain.com:6140/rest/admin/personalizeMe</value>
</defaultValue>
</string>
</dict>
</managedAppConfiguration>
Most MDM solutions will allow a set of variables that can also be used. In the above example, {SerialNumber} is a variable value that will be substituted at deployment time. Variables are dependent on what the MDM solution provides but things like device serial number, etc. are common.
The bundleId is specific to the client application build and should be set accordingly.
For testing purposes, when running the client application in the iOS simulator, parameters can be set without use of an MDM solution by utilizing the simctl command. The following example sets the autoPersonalizeUrl parameter in the simulator just as MDM would set it. See the simctl documentation for additional details.
xcrun simctl spawn booted defaults write com.jumpmind.commerce.dev com.apple.configuration.managed -dict 'autoPersonalizeUrl' 'http://localhost:6140/rest/admin/personalizeMe'
ZeroConf Auto Personalization Provider¶
The ZeroConf personalization provider is deprecated and will be discontinued in a future release.